Diferència entre revisions de la pàgina «Pàgina principal»
m (→Node RED) |
m (→VPS) |
||
| (203 revisions intermèdies per 15 usuaris que no es mostren) | |||
| Línia 1: | Línia 1: | ||
| − | = Node-RED = | + | <span style="font-size:500%">things.cat</span><BR> |
| + | <span style="font-size:300%">Una pàgina pràctica sobre la Internet de les Coses</span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Dispositius IoT. Maquinari i microprogramari = | ||
| + | Al '''maquinari''' li diem'' '''hardware''' ''en anglès. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Al '''microprogramari''' li diem'' '''firmware''' ''en anglès. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''IoT''' és l'acrònim d'''Internet of Things''. En català abreujat li podríem dir '''IdC''' per a referir-nos a '''la Internet de les Coses'''. En el moment d'escriure aquest text, la comunitat catalanoparlant sembla haver optat per referir-se als '''dispositius de la Internet de les Coses''' com a '''dispositius IoT'''. Si el [https://www.termcat.cat/ca/neoloteca/ termcat] es pronuncia de manera diferent, provaré d'adaptar la terminologia. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Placa IoT-02 == | ||
| + | [https://www.binefa.com/index.php/Placa_IoT-02 Placa_IoT-02] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Controladors == | ||
| + | Als '''controladors''' els hi diem'' '''drivers''' ''en anglès. | ||
| + | |||
| + | El xip '''FT232''' ha estat durant molt de temps el xip més comú per convertir d''''USB a UART'''. Fins al punt que se'n van fer còpies pirates. Una actualització del sistema operatiu privatiu Windows va explotar una característica dels xips pirates: els xips pirates tenien el registre d'identificació USB de lectura i escriptura i l'original era tan sols de lectura. L'actualització que va fer Windows provocava l'escriptura d'aquest registre i hi escrivia un zero, que feia que el sistema operatiu ho identifiqués com a concentrador USB i no com a controlador d'UART, fent que el maquinari quedés inservible. A l'any 2014 em vaig veure atrapat amb uns quants Arduino Nano que duien aquest xip pirata i vaig escriure [https://binefa.cat/blog/?p=80 How to recover bricked fake FT232] per a poder-los reprogramar i poder-los fer servir amb sistemes operatius lliures GNU/Linux. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A partir d'aquell moment, bona part de les plaques de fabricació xinesa van començar a dur, massivament, el xip '''CH340''' per a convertir d'USB a UART. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Controlador CH340]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Controlador FT232]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == C / C++ == | ||
| + | [https://github.com/jordibinefa/arduino-IDE-libraries Biblioteques per Arduino, ESP8266 i ESP32] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/jordibinefa/arduino-IDE-codes Codis per Arduino, ESP8266 i ESP32] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === ESP8266 === | ||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Afegint_la_targeta_ESP8266_a_l%27IDE_d%27Arduino Afegint la targeta ESP8266 a l'IDE d'Arduino] (NodeMCU1.0) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/jordibinefa/arduino-IDE-codes/tree/master/esp8266_udpServer_01b esp8266_udpServer_01.ino] Codi UDP per a ESP8266 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=MQTT_a_l%27ESP8266 MQTT a l'ESP8266] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === ESP32 === | ||
| + | [https://github.com/jordibinefa/arduino-IDE-codes/tree/master/esp32_udpServer_01b esp32_udpServer_01b] Codi UDP per a ESP32 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/jordibinefa/arduino-IDE-codes/tree/master/esp32_i2cScanner_02 esp32_i2cScanner_02.ino Adreces de dispositius I2C connectats] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/modbus/rtu/esp32/ Exemple de ModBus RTU fent servir NodeRED i ESP32 (amb la placa IoT PLB)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://techtutorialsx.com/2017/05/06/esp32-arduino-creating-a-task/ ESP32 Arduino: Creating a FreeRTOS task] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://savjee.be/2020/01/multitasking-esp32-arduino-freertos/ Multitasking on ESP32 with Arduino and FreeRTOS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Modbus ==== | ||
| + | [https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/api-reference/peripherals/uart.html#overview-of-rs485-specific-communication-options Overview of RS485 specific communication options] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://pastebin.com/2PtWJvd6 Example setting RS485 at half duplex mode] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/jordibinefa/IoT-02/tree/master/codes/IoT-02_11_modbus_bme280_02 Code IoT-02_11_modbus_bme280_02] using RS485 at half duplex mode | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== ESP-IDF ==== | ||
| + | [https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/get-started/ Get Started] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://docs.platformio.org/en/latest/tutorials/espressif32/espidf_debugging_unit_testing_analysis.html Get started with ESP-IDF and ESP32-DevKitC: debugging, unit testing, project analysis] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Python == | ||
| + | === Accés al maquinari de la Raspberry Pi emprant Python === | ||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Com_connectar-hi_pantalles_OLED_SSD1306_(128x64) Com connectar-hi pantalles OLED SSD1306 (128x64)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=%C3%9As_d%27entrades_anal%C3%B2giques_amb_l%27ADS115_controlant_sortides_PWM Ús d'entrades analògiques amb l'ADS115 controlant sortides PWM] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Micropython === | ||
| + | [https://blog.miguelgrinberg.com/post/micropython-and-the-internet-of-things-part-i-welcome Micropython and the Internet of Things] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/micropython/micropython/tree/master/ports/esp8266 MicroPython port to ESP8266] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/micropython/micropython/tree/master/ports/esp32 MicroPython port to the ESP32] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://icircuit.net/esp32-micropython-getting-started/1999 ESP32 – Getting started with MicroPython] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://hackernoon.com/get-on-the-good-foot-with-micropython-on-the-esp32-decdd32c4720 Get on the Good Foot with MicroPython on the ESP32] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://hackernoon.com/get-on-the-good-foot-with-micropython-part-2-e1f2efaad50b Exemple en micropython de comunicació MQTT amb un ESP32 i el sensor DS18B20 (One Wire Interface)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/gloveboxes/ESP32-MicroPython-BME280-MQTT-Sample Exemple en micropython de comunicació MQTT amb un ESP32 i el sensor BME280 (I2C)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === CircuitPython === | ||
| + | [https://learn.adafruit.com/circuitpython-with-esp32-quick-start CircuitPython on ESP32 Quick Start] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Sistemes operatius encastats == | ||
| + | === Raspbian === | ||
| + | [https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/computers/remote-access.html Remote Access] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://randomnerdtutorials.com/how-to-install-mosquitto-broker-on-raspberry-pi/ How to Install Mosquitto Broker on Raspberry Pi] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Adaptaci%C3%B3_per_a_que_la_Raspberry_Pi_funcioni_com_a_punt_d%27acc%C3%A9s_donant_adreces_IP_de_classe_B Adaptació per a que la Raspberry Pi funcioni com a punt d'accés donant adreces IP de classe B] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Instal%C2%B7laci%C3%B3_dels_nodes_node-red-contrib-ttn_i_node-red-contrib-modbustcp-no-pooling_a_la_Raspberry_Pi Instal·lació dels nodes node-red-contrib-ttn i node-red-contrib-modbustcp-no-pooling a la Raspberry Pi] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Instal%C2%B7laci%C3%B3_de_l%27OPC-UA_a_la_Raspberry_Pi,_fent_servir_Python,_i_control_des_d%27Indusoft Instal·lació de l'OPC-UA a la Raspberry Pi, fent servir Python, i control des d'Indusoft] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Pr%C3%A0ctica_de_connexi%C3%B3_remota_a_una_Raspberry_Pi Pràctica de connexió remota a una Raspberry Pi] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://core-electronics.com.au/guides/read-only-raspberry-pi/ Read-Only Raspberry Pi - Never Corrupt your Micro-SD Card] | ||
| + | ==== Compilació creuada de Qt6.8.0 per Raspberry Pi 3/4/5 amb ''docker'' ==== | ||
| + | [[Compilació creuada de Qt6.8.0 per Raspberry Pi 3/4/5 amb docker]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Mongoose OS === | ||
| + | [https://mongoose-os.com/docs/mongoose-os/quickstart/setup.md Guia ràpida d'introducció a Mongoose OS][en] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Sensors == | ||
| + | [[Sensors de so]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Control remot dels dispositius IoT. Programari = | ||
| + | Al '''programari''' li diuen'' '''software''' ''en anglès. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Protocols == | ||
| + | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/teoria/ethernetTcpUdp_00.pdf TCP/UDP Capa de transport d'Ethernet] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Instal·lació d'un servidor de sòcols web a un Debian amb Apache]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === MQTT(S) === | ||
| + | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/teoria/mqtt_00.pdf Introducció a MQTT] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.steves-internet-guide.com/mqtt/ Beginners Guide To The MQTT Protocol] by Steve's Internet Guide | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.rs-online.com/designspark/mqtt MQTT] explained by Andy Stanford-Clark (co-inventor of MQTT). Article written in 2017, and refering to v3.1.1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.hivemq.com/mqtt-5/ MQTT 5 Essentials] by HiveMQ | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.steves-internet-guide.com/mqtt-hosting-brokers-and-servers/ MQTT Brokers/Servers and Cloud Hosting Guide] by Steve's Internet Guide | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://mqtt-explorer.com/ MQTT Explorer] An all-round MQTT client that provides a structured topic overview | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/pixavier/mqtt4snap MQTT a Snap!] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Public MQTT(S) brokers ==== | ||
| + | [http://test.mosquitto.org/ mosquitto] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.hivemq.com/public-mqtt-broker/ HiveMQ MQTT broker] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://diyprojects.io/8-online-mqtt-brokers-iot-connected-objects-cloud/ MQTT brokers online with a free offer to test and connect IoT to the internet] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== MQTT(S) implementations ==== | ||
| + | [http://binefa.com/index.php?title=MQTTS_y_NodeRED MQTTS y NodeRED] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_MQTT_implementations Comparison of MQTT implementations] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://test.mosquitto.org/ test.mosquitto.org] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.emqx.io/ emqx.io] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://vernemq.com/ VerneMQ] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Webhooks === | ||
| + | [https://hookdeck.com/guides/webhooks/what-are-webhooks-how-they-work What Are Webhooks And How They Work] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Exemple bàsic de funcionament de Webhooks. Servidor i client en node.js]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Programació local (ordinadors d'escriptori i dispositius mòbils) == | ||
| + | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/mqtt/MQTT_Dash/ Configuració de MQTT Dash (aplicació per Android)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Mosquitto local a l'ordinador === | ||
| + | [https://www.vultr.com/docs/how-to-install-mosquitto-mqtt-broker-server-on-ubuntu-16-04 How to Install Mosquitto MQTT Broker/Server on Ubuntu 16.04] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.steves-internet-guide.com/downloads/ Instal·lació de Mosquitto a Windows] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Per a actualitzar les claus dels dipòsits de Debian: | ||
| + | wget http://repo.mosquitto.org/debian/mosquitto-repo.gpg.key | ||
| + | sudo apt-key add mosquitto-repo.gpg.key | ||
| + | |||
| + | === SCADA === | ||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=SCADA_fent_servir_Python_QML_i_Arduino SCADA fent servir Python QML i Arduino] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Núvol == | ||
| + | === Instal·lació de Node.js i npm === | ||
| + | [https://github.com/nodesource/distributions/blob/master/README.md Instal·lació de node i npm] | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~$ '''sudo bash''' | ||
| + | root@iot-ecat:/home/ecat# '''curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | bash -''' | ||
| + | root@iot-ecat:/home/ecat# '''apt install -y nodejs''' | ||
| + | root@iot-ecat:/home/ecat# '''exit''' | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~$ '''node --version''' | ||
| + | v14.15.4 | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~$ '''npm -- version''' | ||
| + | 6.14.10 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Node-RED === | ||
[https://binefa.cat/IoT/nodeRed/nodeRed01.pdf Introducció al Node-RED] | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/nodeRed/nodeRed01.pdf Introducció al Node-RED] | ||
[[Gestió de Node-RED]] | [[Gestió de Node-RED]] | ||
| − | = MQTT(S) = | + | [https://www.aprendiendoarduino.com/cursos/node-red-developer-para-iot-nivel-i/ Node-RED Developer para IoT. Nivel I] |
| − | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/ | + | |
| + | ==== Instal·lació i funcionament del NodeRed autònom ==== | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~$ '''mkdir bin''' | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~$ '''cd bin''' | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin$ '''sudo apt install unzip''' | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin$ '''mkdir nodered-ui''' | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin$ '''cd nodered-ui''' | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin/nodered-ui$ '''wget https://www.binefa.cat/IoT/nodeRed/node_red_ui.zip''' | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin/nodered-ui$ '''unzip node_red_ui.zip''' | ||
| + | ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin/nodered-ui$ '''node node_modules/node-red/red.js --userDir node_modules/node-red/data --settings node_modules/node-red/settings.js -v --port 2222 --title elmeuTitol --safe flows_meuTitol.json''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== UDP ==== | ||
| + | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/nodeRed/prj/udpServer/udpServer_nodered_code.txt Codi NodeRED per a esp8266_udpServer_01.ino i esp32_udpServer_01b] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== MQTT(S) ==== | ||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=MQTT_i_MQTTS MQTT i MQTTS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/nodeRed/prj/mqtt_esp8266_esp32/ex00/ Exemple amb MQTT i NodeRED emprant ESP8266 i ESP32] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/nodeRed/prj/mqtt_esp8266_esp32/ex01/ Exercici amb MQTT i NodeRED emprant ESP8266] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Elevador en Snap! controlat remotament amb MQTT mitjançant NodeRED fent crides HTTP]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://mqtt-explorer.com/ MQTT Explorer] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Telegram ==== | ||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Un_exemple_d%27us_de_Telegram_amb_el_NodeRed Un exemple d'us de Telegram amb el NodeRed] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Modbus TCP ==== | ||
| + | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/modbus/ Arxius per treballar amb Modbus TCP] [https://www.binefa.cat/php/doc/modbus/ El segon vídeo explica i compara Modbus RTU i Modbus TCP] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://binefa.cat/IoT/nodeRed/prj/modbusCtrl/ ModBus TCP al NodeRED] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Alguns nodes extra ==== | ||
| + | [https://flows.nodered.org/node/node-red-contrib-google-sheets node-red-contrib-google-sheets] | ||
| − | [https:// | + | [https://github.com/sammachin/node-red-contrib-google-sheets node-red-contrib-google-sheets al Github] |
| − | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title= | + | === Sistemes d'emmagatzematge i visualització === |
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=InfluxDB Base de dades de sèries temporals InfluxDB] | ||
| − | [ | + | [http://docs.grafana.org/installation/debian/ Instal·lació de Grafana a Debian][en] |
[[Sentilo]] | [[Sentilo]] | ||
| − | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title= | + | === Xarxes d'àrea estesa de baix consum (LPWAN) === |
| + | ==== Conceptes teòrics ==== | ||
| + | [https://ca.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xarxa_de_llarg_abast Xarxa de llarg abast (WAN)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ca.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chirp_spread_spectrum Espectre eixamplat (Chirp Spread Spectrum)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ca.wikipedia.org/wiki/Espectre_eixamplat_per_seq%C3%BC%C3%A8ncia_directa Espectre eixamplat per seqüència directa (DSSS)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ca.wikipedia.org/wiki/Espectre_eixamplat_per_salt_de_freq%C3%BC%C3%A8ncia Espectre eixamplat per salt de freqüència (FHSS)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LPWAN What is LPWAN?] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://cms.edn.com/ContentEETimes/Documents/EDN/LP%20WAN%20Comparison%20Table%20final.pdf Comparison table of Low Power WAN alternatives] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== LoRa ==== | ||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=LoRa LoRa] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== SigFox ==== | ||
| + | [https://docs.pycom.io/chapter/tutorials/sipy/register.html Registering SiPy with Sigfox] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Interacció amb SiPy1.0r de pycom]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Antenes ==== | ||
| + | [https://youtu.be/CJNq2I_PDHQ Andreas Spiess video: "#182 ESP32 Lora Boards: What you need to know before you buy (incl. Antenna knowledge)"] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Bots === | ||
| + | ==== Bot de Telegram ==== | ||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Bot_de_Telegram Bot de Telegram] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Bot de Mastodon ==== | ||
| + | No totes les instàncies de [https://ca.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mastodon_(xarxa_social) Mastodon] faciliten la instal·lació de bots. Per a fer les primeres passes us recomano aquesta [https://botsin.space/ instància pensada per allotjar bots de Mastodon]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://botsin.space/@siarq_sensors Exemple de bot de Mastodon] per a fer lectures de sensors cada hora. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://gist.github.com/aparrish/661fca5ce7b4882a8c6823db12d42d26 Getting credentials for the Mastodon API with Mastodon.py, step by step] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === VPS === | ||
| + | [[Introducció als contenidors docker]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Servidor intermediari invers]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Mediawiki]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File Browser]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Apache i PHP]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Redireccions a subdomini]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Mastodon]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://medium.com/himinds/mqtt-broker-with-secure-websocket-using-traefik-docker-compose-and-lets-encrypt-2b8e32207555 MQTT broker with Secure WebSocket using Traefik, Docker Compose and Let’s Encrypt] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://broker.binefa.cat/wordpressTraefik.html Guia completa: Instal·lació de Traefik + WordPress + PHP + MariaDB des de zero] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://broker.binefa.cat/guia.html Guia completa: Instal·lació de Mosquitto MQTT amb Traefik en VPS] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Moodle a un servidor intermediari invers emprant Dockers]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Node-RED a un servidor intermediari invers emprant Dockers]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Snap! a un servidor intermediari invers emprant Dockers]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[VPN WireGuard]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Snap! == | ||
| + | [https://github.com/jmoenig/Snap Snap! al GitHub] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://snap.berkeley.edu/snap/snap.html Versió pública d'Snap! '''amb''' SSL]. Amb el JavaScript desactivat per defecte. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://extensions.snap.berkeley.edu/snap/snap.html Versió pública d'Snap! '''sense''' SSL]. Amb el JavaScript desactivat per defecte. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === JavaScript per defecte === | ||
| + | Per raons de seguretat, s'ha desactivat el JavaScript per defecte. Si us munteu el vostre propi servei al núvol, per a poder cridar programes vostres amb funcions amb JavaScript, heu d'afegir aquesta línia, en negreta, a l'arxiu ''[https://github.com/jmoenig/Snap/blob/master/snap.html snap.html]'': | ||
| + | <script> | ||
| + | '''Process.prototype.enableJS = true;''' // <-- Per a tenir seleccionat el JS per defecte | ||
| + | var world; | ||
| + | window.onload = function () { | ||
| + | if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) { | ||
| + | navigator.serviceWorker.register('sw.js'); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | world = new WorldMorph(document.getElementById('world')); | ||
| + | new IDE_Morph().openIn(world); | ||
| + | loop(); | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | function loop() { | ||
| + | requestAnimationFrame(loop); | ||
| + | world.doOneCycle(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </script> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === MQTT for Snap! === | ||
| + | [https://github.com/pixavier/mqtt4snap MQTT4Snap !], desenvolupat per en Xavier Pi. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://snap.berkeley.edu/snap/snap.html#open:https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pixavier/mqtt4snap/master/HelloWorld.xml Hello World emprant MQTT '''amb''' SSL] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://extensions.snap.berkeley.edu/snap/snap.html#open:http://raw.githubusercontent.com/pixavier/mqtt4snap/master/HelloWorld_NoSSL.xml Hello World emprant MQTT '''sense''' SSL] | ||
| + | === Intel·ligència Artificial === | ||
| + | * [https://snap.berkeley.edu/snap/snap.html#open:https://xavierpi.com/ia/ia.xml Connexió amb Gemini] Cal una [https://aistudio.google.com/app/apikey clau d'API (API key)] ([https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/quickstart?lang=python Guia ràpida d'ús a l'API de Gemini]) | ||
| + | <!-- AIzaSyBINpQKh7Sj8WyIV-PmNfo157Pg8LQr8JY --> | ||
| + | * [https://ecraft2learn.github.io/ai/AI-Teacher-Guide/chapter-2.html Reconeixement de veu amb Snap!] ([https://ecraft2learn.github.io/ai/snap/snap.html?project=listening&editMode Accés directe al projecte amb Snap!]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Una aproximació a OPC-UA = | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[OPC-UA]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Placa IoT-02 = | ||
| + | [[Placa IoT-02]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Programació remota (OTA) == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Esp32Ota.png|center|Programacio OTA de la placa IoT-02]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Dos programes de prova de programació remota === | ||
| + | [https://www.binefa.cat/training/iot02/ota/IoT-02_OTAWebUpdater_01.zip IoT-02_OTAWebUpdater_01] (Fa pampallugues el led blanc) Per a que us funcioni, haureu d'actualitzar el codi amb el vostre nom de xarxa sense fils (SSID) i la vostra contrasenya d'accés. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.binefa.cat/training/iot02/ota/IoT-02_OTAWebUpdater_02.zip IoT-02_OTAWebUpdater_02] (Fa pampallugues el led verd) Per a que us funcioni, haureu d'actualitzar el codi amb el vostre nom de xarxa sense fils (SSID) i la vostra contrasenya d'accés. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Programació a la vora (''edge'') === | ||
| + | L'ordinador a la vora (''edge'') pot ser un ordinador normal, habitualment de poca potència, del tipus Raspberry Pi. | ||
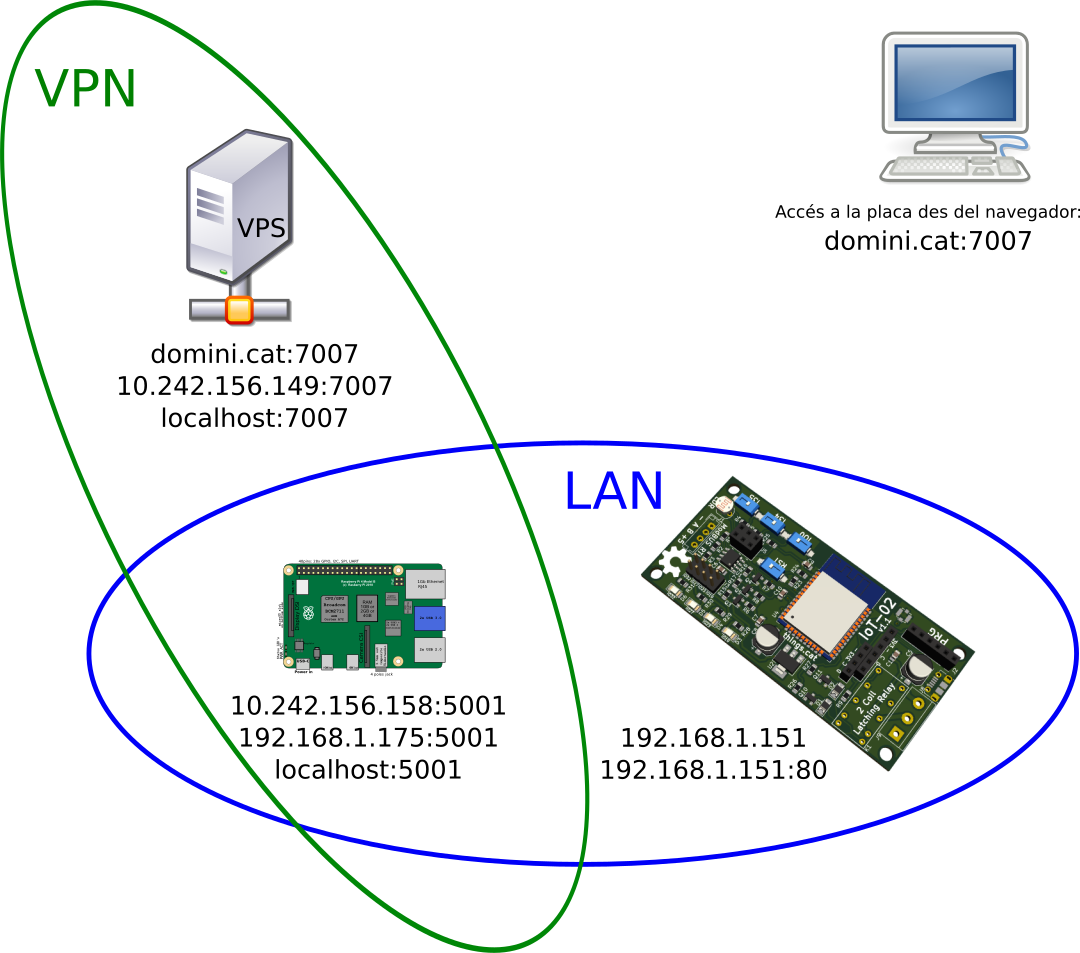
| + | |||
| + | Per a tenir visibilitat externa de la pàgina web servida per la placa IoT-02 (per exemple amb la IP 192.168.1.151:80), ho redireccionarem a un port ( 192.168.1.151:80 --> localhost:5001 ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Per a fer funcionar [https://www.binefa.cat/training/iot02/ota/edge/simple-port-forwarding.js simple-port-forwarding.js] caldrà haver afegit el paquet '''http-proxy''': | ||
| + | |||
| + | npm install http-proxy | ||
| + | |||
| + | El codi nodejs de redireccionament (suposant que la placa IoT-02 ha adquirit l'adreça IP 192.168.1.151): | ||
| + | var httpProxy = require('http-proxy'); | ||
| + | var targetHost = '192.168.1.151'; | ||
| + | var portOrigen = 80; | ||
| + | var portDesti = 5001; | ||
| + | httpProxy.createProxyServer({target:'http://' + targetHost + ':' + portOrigen}).listen(portDesti); | ||
| + | |||
| + | Per a fer aquest redireccionador sigui un servei, es copia [https://www.binefa.cat/training/iot02/ota/edge/myForwardingService.service myForwardingService.service] a la carpeta '''/etc/systemd/system''' o el fem de nou amb un editor: | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd /etc/systemd/system | ||
| + | sudo nano [https://www.binefa.cat/training/iot02/ota/edge/myForwardingService.service myForwardingService.service] | ||
| + | sudo chmod 755 myForwardingService.service | ||
| + | sudo systemctl daemon-reload | ||
| + | sudo systemctl '''start''' myForwardingService | ||
| + | |||
| + | Per a veure l'estat del servei: | ||
| + | systemctl '''status''' myForwardingService | ||
| + | |||
| + | I per a fer que el servei es posi en marxa al reiniciar l'ordinador a la vora: | ||
| + | sudo systemctl '''enable''' myForwardingService | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Programació al núvol === | ||
| + | Mitjançant una xarxa virtual privada (VPN) de l'estil [https://www.zerotier.com/ ZeroTier] podem fer que l'ordinador a la vora i l'ordinador al núvol comparteixin la mateixa xarxa. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Suposant que l'ordinador a la vora té la IP 10.242.156.158, podem redireccionar-hi 10.242.156.158:5001 --> localhost:7007 : | ||
| + | |||
| + | var httpProxy = require('http-proxy'); | ||
| + | var targetHost = '10.242.156.158'; | ||
| + | var portOrigen = 5001; | ||
| + | var portDesti = 7007; | ||
| + | httpProxy.createProxyServer({target:'http://' + targetHost + ':' + portOrigen}).listen(portDesti); | ||
| + | |||
| + | I així tenim accés remot des del núvol, connectant mitjançant l'ordinador a la vora que es connecta a la placa IoT-02. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Per accedir-hi des del navegador, escriviu a la URL: | ||
| + | <nom_de_domini>:7007 | ||
| + | Això visualitzarà el que presenta l'ordinador a la vora (la IP és la VPN a l'ordinador a la vora): | ||
| + | 10.242.156.158:5001 | ||
| + | Que al seu temps presenta el servei pel port 80 de la placa IOT-02 connectada a la mateixa xarxa local que l'ordinador a la vora: | ||
| + | 192.168.1.151 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Els tres mètodes de programació OTA de l'ESP32 === | ||
| + | [https://www.programmersought.com/article/90864120754/ How to implement OTA online update of ESP32 firmware] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == MicroPython == | ||
| + | [https://www.digikey.es/en/maker/projects/micropython-basics-load-files-run-code/fb1fcedaf11e4547943abfdd8ad825ce MicroPython Basics: Load Files & Run Code] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://warped3.substack.com/p/compiling-micropython-with-espressif Compiling microPython with espressif SDK 4.4 for ESP32] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/esp32/tutorial/intro.html Getting started with MicroPython on the ESP32] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/micropython/micropython The MicroPython project] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://cdn-learn.adafruit.com/downloads/pdf/micropython-basics-loading-modules.pdf MicroPython Basics: Loading Modules] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/mrvelic/micropython/commit/e6a8481e31d64845b4774ecc2f5b973dacb90351 esp32/machine_uart: Add uart_mode/flow_ctrl args to UART construct/init] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/robert-hh/FTP-Server-for-ESP8266-ESP32-and-PYBD uftpd: small FTP server for ESP8266, ESP32 and Pyboard D] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://electronicsinnovation.com/connect-esp32-to-ubidots-using-micropython-over-mqtt-with-visual-studio-code/ Connect ESP32 to Ubidots using Micropython over MQTT with Visual Studio Code] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/peterhinch Peter Hinch's GitHub] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wolles-elektronikkiste.de/en/programming-the-esp32-with-micropython Programming the ESP32 with MicroPython] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://awesome-micropython.com/ A curated list of awesome MicroPython libraries, frameworks, software and resources] | ||
| + | === asyncio === | ||
| + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5VLvmA__2v0 How to Use Asyncio in MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico) | Digi-Key Electronics] | ||
| + | === Threads === | ||
| + | [https://github.com/kevinmcaleer/threads Micropython thread tutorial] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QeDnjcdGrpY Video: Micropython Threads - Use Both Cores, on Raspberry Pi Pico and ESP32] | ||
| + | === MQTT === | ||
| + | [https://bhave.sh/micropython-mqtt/ Secrets of MicroPython: MQTT on ESP32] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wokwi.com/projects/341892004923310676 Exemple MQTT sobre micropython funcionant al wokwi] ([https://wokwi.com/projects/341895401936257620 Un exemple més compacte]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Modbus === | ||
| + | ==== Modifying source code ==== | ||
| + | [https://github.com/brainelectronics/micropython-modbus MicroPython Modbus library] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Modbus control signal able to send or receive messages can be controlled directly by UART. To do that, file [https://github.com/mrvelic/micropython/blob/master/ports/esp32/machine_uart.c machine_uart.c] should be changed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Changes to be able to use Tx/Rx MAX3485 pin: [https://github.com/mrvelic/micropython/commit/e6a8481e31d64845b4774ecc2f5b973dacb90351 esp32/machine_uart: Add uart_mode/flow_ctrl args to UART construct/init] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Information about Modbus an MicroPython has been got from this forum: https://github.com/micropython/micropython/pull/5567 | ||
| + | ==== Based on pycom-modbus from pycom ==== | ||
| + | [https://github.com/danjperron/micropython-modbus Modbus Master library for MicroPython ESP32 devices] | ||
| + | === LoRa === | ||
| + | [https://github.com/martynwheeler/u-lora This is a port of raspi-lora for micropython] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = IoT-Vertebrae = | ||
| + | == Raspberry == | ||
| + | [[Configuració de la WiFi a la Raspberry Pi emprant nmtui]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Reconnexió automàtica a la WiFi]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[WireGuard VPN]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Exemples pràctics = | ||
| + | == Sensor ModBus de temperatura i humitat CWT-TH03S == | ||
| + | [https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005001404952412.html CWT-TH03S a AliExpress] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Accés ModBus al sensor de temperatura i humitat CWT-TH03S]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = SBC = | ||
| + | == PocketBeagle == | ||
| + | === Grove Kit === | ||
| + | ==== Visió general ==== | ||
| + | [https://beagleboard.org/Kits/Grove Informació comercial del Grove Kit] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://beagleboard.org/pocket Informació comercial de la PocketBeagle] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/beagleboard/pocketbeagle/wiki Wiki de la PocketBeagle] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/beagleboard/pocketbeagle/wiki/System-Reference-Manual System Reference Manual] <---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://beagleboard.org/latest-images Darreres imatges per a les SD] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/beagleboard/capes/tree/master/pocketbeagle/Grove Disseny del Grove Cape] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Primera connexió a la xarxa sense fils ==== | ||
| + | debian@beaglebone:/var/lib/cloud9$ '''sudo connmanctl'''⏎ | ||
| + | [sudo] password for debian: temppwd⏎ | ||
| + | connmanctl> '''scan wifi'''⏎ | ||
| + | Scan completed for wifi | ||
| + | connmanctl> '''services'''⏎ | ||
| + | MyWifi wifi_1234567890_1234567890123456_managed_psk | ||
| + | connmanctl> '''agent on'''⏎ | ||
| + | Agent registered | ||
| + | connmanctl> '''connect wifi_1234567890_1234567890123456_managed_psk'''⏎ | ||
| + | Agent RequestInput wifi_1234567890_1234567890123456_managed_psk | ||
| + | Passphrase = [ Type=psk, Requirement=mandatory, Alternates=[ WPS ] ] | ||
| + | WPS = [ Type=wpspin, Requirement=alternate ] | ||
| + | Passphrase? '''MySecretPassphrase'''⏎ | ||
| + | Connected wifi_1234567890_1234567890123456_managed_psk | ||
| + | connmanctl> '''quit'''⏎ | ||
| + | debian@beaglebone:/var/lib/cloud9$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Tutorials ==== | ||
| + | [https://github.com/beagleboard/cloud9-examples/blob/master/PocketBeagle/Grove/workshop-handouts.md Blink PocketBeagle on-board USRx LED] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://github.com/beagleboard/cloud9-examples/tree/master/PocketBeagle/Grove Exemples] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Formació = | ||
| + | [https://www.binefa.com/index.php/IoT_amb_Arduino_i_Raspberry_Pi._Microcontroladors_d%27%C3%BAs_professional._Curs_Presencial._Edici%C3%B3_de_mar%C3%A7_de_2022 IoT amb Arduino i Raspberry Pi. Microcontroladors d'ús professional. Curs Presencial. Edició de març de 2022] - [https://formacio.eic.cat/cursos/1123577 Formació al Col·legi d'Enginyers Industrials de Catalunya] (30 / març / 2022) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.binefa.com/index.php/Sistemes_encastats_d%27escala_petita_i_mitjana._Edici%C3%B3_d%27octubre_2021 Sistemes encastats d'escala petita i mitjana. Edició d'octubre 2021] (20 / octubre / 2021) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.binefa.com/index.php/Nodes_sensors_(motes)_i_passarel%C2%B7les_(gateways)_IoT_(22_de_mar%C3%A7_de_2022) Nodes sensors (motes) i passarel·les (gateways) IoT (22 de març de 2022)] pel [https://www.fundaciocim.org/ca/formacio/master-mtdi Màster en Transformació Digital en la Indústria] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://www.binefa.com/index.php/Tecnolog%C3%ADas_IoT,_Hands_on_y_MVP_(2022) Tecnologías IoT, Hands on y MVP (2022)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.binefa.com/index.php?title=Diada_de_la_Llibertat_del_Maquinari_(Edici%C3%B3_2021) Diada de la Llibertat del Maquinari (Edició 2021)] (17 d'abril de 2021) | ||
| + | |||
| + | UPC-School - Màster Industria 4.0 [http://binefa.com/index.php?title=Tecnolog%C3%ADas_IoT,_Hands_on_y_MVP_(2021) Tecnologías IoT, Hands on y MVP (2021)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.binefa.com/index.php?title=Nodes_sensors_(motes)_i_passarel%C2%B7les_(gateways) Nodes sensors (motes) i passarel·les (gateways)] pel [https://www.fundaciocim.org/ca/formacio/master-mtdi Màster en Transformació Digital en la Indústria] (23 de març de 2021) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.binefa.com/index.php?title=Monitoritzaci%C3%B3_de_la_qualitat_de_l%27aire_mesurant_CO2_i_VOC_amb_LoRa Monitorització de la qualitat de l'aire mesurant CO2 i VOC amb LoRa] (9 de gener de 2021) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Curset introductori d'Internet de les Coses per ADTelecom]] (Comença el 5 de novembre de 2020) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.binefa.com/index.php?title=%C3%9As_de_les_dades_generades_pels_sensors_LoRaWAN_i_arquitectura_del_sistema._Rub%C3%AD_2020 Ús de les dades generades pels sensors LoRaWAN i arquitectura del sistema. Rubí, 17 de juny de 2020] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Curset_a_TE_Connectivity_del_4_de_mar%C3%A7_de_2020 Curset a TE Connectivity del 4 de març de 2020] a [https://www.te.com/ TE Connectivity] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Introducci%C3%B3_r%C3%A0pida_a_LoRaWAN_i_The_Things_Network Introducció ràpida a LoRaWAN i The Things Network] (Ajuntament de Viladecans, 19 de febrer de 2020) | ||
| + | |||
| + | UPC-School - Màster Industria 4.0 [http://www.binefa.com/index.php?title=Tecnolog%C3%ADas_IoT,_Hands_on_y_MVP_(2020) Tecnologías IoT, Hands on y MVP (2020)] | ||
| + | |||
| + | UPC-School - 21802500 - Màster Industria 4.0 [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Tecnolog%C3%ADas_IoT,_Hands_on_y_MVP Tecnologías IoT, Hands on y MVP] (2019) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Introducci%C3%B3_r%C3%A0pida_a_LoRaWAN_i_The_Things_Network Introducció ràpida a LoRaWAN i The Things Network] a l'[http://www.icm.csic.es/ Institut de Ciències del Mar] (27 / setembre / 2018 i 25 / setembre / 2019) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://wiki.binefa.cat/index.php?title=Introducci%C3%B3_a_Internet_de_les_Coses_-_juny_2018 Introducció a Internet de les Coses - juny 2018] (Curset de formació per a professors de CF realitzat a l'[https://agora.xtec.cat/iesramblaprim/ Institut Rambla Prim]) | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | [[Sunna LoRa RMM v3.0]] | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Xifratge = | ||
| + | [[Eines de xifratge en línia]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Opinió = | ||
| + | [http://www.xavierpi.com/mi40/HaciaUnIoT_democraticoYEfectivo.pdf Hacia un Internet de las Cosas democrático y efectivo] per Xavier Pi (octubre 2018) | ||
| + | |||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| + | [[Auxiliar]] | ||
<strong>MediaWiki s'ha instal·lat.</strong> | <strong>MediaWiki s'ha instal·lat.</strong> | ||
Consulteu la [https://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Help:Contents Guia d'Usuari] per a més informació sobre com utilitzar aquest programari wiki. | Consulteu la [https://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Help:Contents Guia d'Usuari] per a més informació sobre com utilitzar aquest programari wiki. | ||
| + | |||
== Primers passos == | == Primers passos == | ||
Revisió de 12:38, 27 nov 2025
things.cat
Una pàgina pràctica sobre la Internet de les Coses
Contingut
- 1 Dispositius IoT. Maquinari i microprogramari
- 2 Control remot dels dispositius IoT. Programari
- 3 Una aproximació a OPC-UA
- 4 Placa IoT-02
- 5 IoT-Vertebrae
- 6 Exemples pràctics
- 7 SBC
- 8 Formació
- 9 Xifratge
- 10 Opinió
Dispositius IoT. Maquinari i microprogramari
Al maquinari li diem hardware en anglès.
Al microprogramari li diem firmware en anglès.
IoT és l'acrònim d'Internet of Things. En català abreujat li podríem dir IdC per a referir-nos a la Internet de les Coses. En el moment d'escriure aquest text, la comunitat catalanoparlant sembla haver optat per referir-se als dispositius de la Internet de les Coses com a dispositius IoT. Si el termcat es pronuncia de manera diferent, provaré d'adaptar la terminologia.
Placa IoT-02
Controladors
Als controladors els hi diem drivers en anglès.
El xip FT232 ha estat durant molt de temps el xip més comú per convertir d'USB a UART. Fins al punt que se'n van fer còpies pirates. Una actualització del sistema operatiu privatiu Windows va explotar una característica dels xips pirates: els xips pirates tenien el registre d'identificació USB de lectura i escriptura i l'original era tan sols de lectura. L'actualització que va fer Windows provocava l'escriptura d'aquest registre i hi escrivia un zero, que feia que el sistema operatiu ho identifiqués com a concentrador USB i no com a controlador d'UART, fent que el maquinari quedés inservible. A l'any 2014 em vaig veure atrapat amb uns quants Arduino Nano que duien aquest xip pirata i vaig escriure How to recover bricked fake FT232 per a poder-los reprogramar i poder-los fer servir amb sistemes operatius lliures GNU/Linux.
A partir d'aquell moment, bona part de les plaques de fabricació xinesa van començar a dur, massivament, el xip CH340 per a convertir d'USB a UART.
C / C++
Biblioteques per Arduino, ESP8266 i ESP32
Codis per Arduino, ESP8266 i ESP32
ESP8266
Afegint la targeta ESP8266 a l'IDE d'Arduino (NodeMCU1.0)
esp8266_udpServer_01.ino Codi UDP per a ESP8266
ESP32
esp32_udpServer_01b Codi UDP per a ESP32
esp32_i2cScanner_02.ino Adreces de dispositius I2C connectats
Exemple de ModBus RTU fent servir NodeRED i ESP32 (amb la placa IoT PLB)
ESP32 Arduino: Creating a FreeRTOS task
Multitasking on ESP32 with Arduino and FreeRTOS
Modbus
Overview of RS485 specific communication options
Example setting RS485 at half duplex mode
Code IoT-02_11_modbus_bme280_02 using RS485 at half duplex mode
ESP-IDF
Get started with ESP-IDF and ESP32-DevKitC: debugging, unit testing, project analysis
Python
Accés al maquinari de la Raspberry Pi emprant Python
Com connectar-hi pantalles OLED SSD1306 (128x64)
Ús d'entrades analògiques amb l'ADS115 controlant sortides PWM
Micropython
Micropython and the Internet of Things
ESP32 – Getting started with MicroPython
Get on the Good Foot with MicroPython on the ESP32
Exemple en micropython de comunicació MQTT amb un ESP32 i el sensor DS18B20 (One Wire Interface)
Exemple en micropython de comunicació MQTT amb un ESP32 i el sensor BME280 (I2C)
CircuitPython
CircuitPython on ESP32 Quick Start
Sistemes operatius encastats
Raspbian
How to Install Mosquitto Broker on Raspberry Pi
Adaptació per a que la Raspberry Pi funcioni com a punt d'accés donant adreces IP de classe B
Instal·lació de l'OPC-UA a la Raspberry Pi, fent servir Python, i control des d'Indusoft
Pràctica de connexió remota a una Raspberry Pi
Read-Only Raspberry Pi - Never Corrupt your Micro-SD Card
Compilació creuada de Qt6.8.0 per Raspberry Pi 3/4/5 amb docker
Compilació creuada de Qt6.8.0 per Raspberry Pi 3/4/5 amb docker
Mongoose OS
Guia ràpida d'introducció a Mongoose OS[en]
Sensors
Control remot dels dispositius IoT. Programari
Al programari li diuen software en anglès.
Protocols
TCP/UDP Capa de transport d'Ethernet
Instal·lació d'un servidor de sòcols web a un Debian amb Apache
MQTT(S)
Beginners Guide To The MQTT Protocol by Steve's Internet Guide
MQTT explained by Andy Stanford-Clark (co-inventor of MQTT). Article written in 2017, and refering to v3.1.1
MQTT 5 Essentials by HiveMQ
MQTT Brokers/Servers and Cloud Hosting Guide by Steve's Internet Guide
MQTT Explorer An all-round MQTT client that provides a structured topic overview
Public MQTT(S) brokers
MQTT brokers online with a free offer to test and connect IoT to the internet
MQTT(S) implementations
Comparison of MQTT implementations
Webhooks
What Are Webhooks And How They Work
Exemple bàsic de funcionament de Webhooks. Servidor i client en node.js
Programació local (ordinadors d'escriptori i dispositius mòbils)
Configuració de MQTT Dash (aplicació per Android)
Mosquitto local a l'ordinador
How to Install Mosquitto MQTT Broker/Server on Ubuntu 16.04
Instal·lació de Mosquitto a Windows
Per a actualitzar les claus dels dipòsits de Debian:
wget http://repo.mosquitto.org/debian/mosquitto-repo.gpg.key sudo apt-key add mosquitto-repo.gpg.key
SCADA
SCADA fent servir Python QML i Arduino
Núvol
Instal·lació de Node.js i npm
ecat@iot-ecat:~$ sudo bash root@iot-ecat:/home/ecat# curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | bash - root@iot-ecat:/home/ecat# apt install -y nodejs root@iot-ecat:/home/ecat# exit ecat@iot-ecat:~$ node --version v14.15.4 ecat@iot-ecat:~$ npm -- version 6.14.10
Node-RED
Node-RED Developer para IoT. Nivel I
Instal·lació i funcionament del NodeRed autònom
ecat@iot-ecat:~$ mkdir bin ecat@iot-ecat:~$ cd bin ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin$ sudo apt install unzip ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin$ mkdir nodered-ui ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin$ cd nodered-ui ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin/nodered-ui$ wget https://www.binefa.cat/IoT/nodeRed/node_red_ui.zip ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin/nodered-ui$ unzip node_red_ui.zip ecat@iot-ecat:~/bin/nodered-ui$ node node_modules/node-red/red.js --userDir node_modules/node-red/data --settings node_modules/node-red/settings.js -v --port 2222 --title elmeuTitol --safe flows_meuTitol.json
UDP
Codi NodeRED per a esp8266_udpServer_01.ino i esp32_udpServer_01b
MQTT(S)
Exemple amb MQTT i NodeRED emprant ESP8266 i ESP32
Exercici amb MQTT i NodeRED emprant ESP8266
Elevador en Snap! controlat remotament amb MQTT mitjançant NodeRED fent crides HTTP
Telegram
Un exemple d'us de Telegram amb el NodeRed
Modbus TCP
Arxius per treballar amb Modbus TCP El segon vídeo explica i compara Modbus RTU i Modbus TCP
Alguns nodes extra
node-red-contrib-google-sheets
node-red-contrib-google-sheets al Github
Sistemes d'emmagatzematge i visualització
Base de dades de sèries temporals InfluxDB
Instal·lació de Grafana a Debian[en]
Xarxes d'àrea estesa de baix consum (LPWAN)
Conceptes teòrics
Espectre eixamplat (Chirp Spread Spectrum)
Espectre eixamplat per seqüència directa (DSSS)
Espectre eixamplat per salt de freqüència (FHSS)
Comparison table of Low Power WAN alternatives
LoRa
SigFox
Interacció amb SiPy1.0r de pycom
Antenes
Bots
Bot de Telegram
Bot de Mastodon
No totes les instàncies de Mastodon faciliten la instal·lació de bots. Per a fer les primeres passes us recomano aquesta instància pensada per allotjar bots de Mastodon.
Exemple de bot de Mastodon per a fer lectures de sensors cada hora.
Getting credentials for the Mastodon API with Mastodon.py, step by step
VPS
Introducció als contenidors docker
MQTT broker with Secure WebSocket using Traefik, Docker Compose and Let’s Encrypt
Guia completa: Instal·lació de Traefik + WordPress + PHP + MariaDB des de zero
Guia completa: Instal·lació de Mosquitto MQTT amb Traefik en VPS
Moodle a un servidor intermediari invers emprant Dockers
Node-RED a un servidor intermediari invers emprant Dockers
Snap! a un servidor intermediari invers emprant Dockers
Snap!
Versió pública d'Snap! amb SSL. Amb el JavaScript desactivat per defecte.
Versió pública d'Snap! sense SSL. Amb el JavaScript desactivat per defecte.
JavaScript per defecte
Per raons de seguretat, s'ha desactivat el JavaScript per defecte. Si us munteu el vostre propi servei al núvol, per a poder cridar programes vostres amb funcions amb JavaScript, heu d'afegir aquesta línia, en negreta, a l'arxiu snap.html:
<script>
Process.prototype.enableJS = true; // <-- Per a tenir seleccionat el JS per defecte
var world;
window.onload = function () {
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
navigator.serviceWorker.register('sw.js');
}
world = new WorldMorph(document.getElementById('world'));
new IDE_Morph().openIn(world);
loop();
};
function loop() {
requestAnimationFrame(loop);
world.doOneCycle();
}
</script>
MQTT for Snap!
MQTT4Snap !, desenvolupat per en Xavier Pi.
Hello World emprant MQTT amb SSL
Hello World emprant MQTT sense SSL
Intel·ligència Artificial
- Connexió amb Gemini Cal una clau d'API (API key) (Guia ràpida d'ús a l'API de Gemini)
- Reconeixement de veu amb Snap! (Accés directe al projecte amb Snap!)
Una aproximació a OPC-UA
Placa IoT-02
Programació remota (OTA)
Dos programes de prova de programació remota
IoT-02_OTAWebUpdater_01 (Fa pampallugues el led blanc) Per a que us funcioni, haureu d'actualitzar el codi amb el vostre nom de xarxa sense fils (SSID) i la vostra contrasenya d'accés.
IoT-02_OTAWebUpdater_02 (Fa pampallugues el led verd) Per a que us funcioni, haureu d'actualitzar el codi amb el vostre nom de xarxa sense fils (SSID) i la vostra contrasenya d'accés.
Programació a la vora (edge)
L'ordinador a la vora (edge) pot ser un ordinador normal, habitualment de poca potència, del tipus Raspberry Pi.
Per a tenir visibilitat externa de la pàgina web servida per la placa IoT-02 (per exemple amb la IP 192.168.1.151:80), ho redireccionarem a un port ( 192.168.1.151:80 --> localhost:5001 )
Per a fer funcionar simple-port-forwarding.js caldrà haver afegit el paquet http-proxy:
npm install http-proxy
El codi nodejs de redireccionament (suposant que la placa IoT-02 ha adquirit l'adreça IP 192.168.1.151):
var httpProxy = require('http-proxy');
var targetHost = '192.168.1.151';
var portOrigen = 80;
var portDesti = 5001;
httpProxy.createProxyServer({target:'http://' + targetHost + ':' + portOrigen}).listen(portDesti);
Per a fer aquest redireccionador sigui un servei, es copia myForwardingService.service a la carpeta /etc/systemd/system o el fem de nou amb un editor:
cd /etc/systemd/system sudo nano myForwardingService.service sudo chmod 755 myForwardingService.service sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl start myForwardingService
Per a veure l'estat del servei:
systemctl status myForwardingService
I per a fer que el servei es posi en marxa al reiniciar l'ordinador a la vora:
sudo systemctl enable myForwardingService
Programació al núvol
Mitjançant una xarxa virtual privada (VPN) de l'estil ZeroTier podem fer que l'ordinador a la vora i l'ordinador al núvol comparteixin la mateixa xarxa.
Suposant que l'ordinador a la vora té la IP 10.242.156.158, podem redireccionar-hi 10.242.156.158:5001 --> localhost:7007 :
var httpProxy = require('http-proxy');
var targetHost = '10.242.156.158';
var portOrigen = 5001;
var portDesti = 7007;
httpProxy.createProxyServer({target:'http://' + targetHost + ':' + portOrigen}).listen(portDesti);
I així tenim accés remot des del núvol, connectant mitjançant l'ordinador a la vora que es connecta a la placa IoT-02.
Per accedir-hi des del navegador, escriviu a la URL:
<nom_de_domini>:7007
Això visualitzarà el que presenta l'ordinador a la vora (la IP és la VPN a l'ordinador a la vora):
10.242.156.158:5001
Que al seu temps presenta el servei pel port 80 de la placa IOT-02 connectada a la mateixa xarxa local que l'ordinador a la vora:
192.168.1.151
Els tres mètodes de programació OTA de l'ESP32
How to implement OTA online update of ESP32 firmware
MicroPython
MicroPython Basics: Load Files & Run Code
Compiling microPython with espressif SDK 4.4 for ESP32
Getting started with MicroPython on the ESP32
MicroPython Basics: Loading Modules
esp32/machine_uart: Add uart_mode/flow_ctrl args to UART construct/init
uftpd: small FTP server for ESP8266, ESP32 and Pyboard D
Connect ESP32 to Ubidots using Micropython over MQTT with Visual Studio Code
Programming the ESP32 with MicroPython
A curated list of awesome MicroPython libraries, frameworks, software and resources
asyncio
How to Use Asyncio in MicroPython (Raspberry Pi Pico) | Digi-Key Electronics
Threads
Video: Micropython Threads - Use Both Cores, on Raspberry Pi Pico and ESP32
MQTT
Secrets of MicroPython: MQTT on ESP32
Exemple MQTT sobre micropython funcionant al wokwi (Un exemple més compacte)
Modbus
Modifying source code
Modbus control signal able to send or receive messages can be controlled directly by UART. To do that, file machine_uart.c should be changed.
Changes to be able to use Tx/Rx MAX3485 pin: esp32/machine_uart: Add uart_mode/flow_ctrl args to UART construct/init
Information about Modbus an MicroPython has been got from this forum: https://github.com/micropython/micropython/pull/5567
Based on pycom-modbus from pycom
Modbus Master library for MicroPython ESP32 devices
LoRa
This is a port of raspi-lora for micropython
IoT-Vertebrae
Raspberry
Configuració de la WiFi a la Raspberry Pi emprant nmtui
Reconnexió automàtica a la WiFi
Exemples pràctics
Sensor ModBus de temperatura i humitat CWT-TH03S
Accés ModBus al sensor de temperatura i humitat CWT-TH03S
SBC
PocketBeagle
Grove Kit
Visió general
Informació comercial del Grove Kit
Informació comercial de la PocketBeagle
System Reference Manual <----
Primera connexió a la xarxa sense fils
debian@beaglebone:/var/lib/cloud9$ sudo connmanctl⏎
[sudo] password for debian: temppwd⏎
connmanctl> scan wifi⏎
Scan completed for wifi
connmanctl> services⏎
MyWifi wifi_1234567890_1234567890123456_managed_psk
connmanctl> agent on⏎
Agent registered
connmanctl> connect wifi_1234567890_1234567890123456_managed_psk⏎
Agent RequestInput wifi_1234567890_1234567890123456_managed_psk
Passphrase = [ Type=psk, Requirement=mandatory, Alternates=[ WPS ] ]
WPS = [ Type=wpspin, Requirement=alternate ]
Passphrase? MySecretPassphrase⏎
Connected wifi_1234567890_1234567890123456_managed_psk
connmanctl> quit⏎
debian@beaglebone:/var/lib/cloud9$
Tutorials
Blink PocketBeagle on-board USRx LED
Formació
IoT amb Arduino i Raspberry Pi. Microcontroladors d'ús professional. Curs Presencial. Edició de març de 2022 - Formació al Col·legi d'Enginyers Industrials de Catalunya (30 / març / 2022)
Sistemes encastats d'escala petita i mitjana. Edició d'octubre 2021 (20 / octubre / 2021)
Nodes sensors (motes) i passarel·les (gateways) IoT (22 de març de 2022) pel Màster en Transformació Digital en la Indústria
Tecnologías IoT, Hands on y MVP (2022)
Diada de la Llibertat del Maquinari (Edició 2021) (17 d'abril de 2021)
UPC-School - Màster Industria 4.0 Tecnologías IoT, Hands on y MVP (2021)
Nodes sensors (motes) i passarel·les (gateways) pel Màster en Transformació Digital en la Indústria (23 de març de 2021)
Monitorització de la qualitat de l'aire mesurant CO2 i VOC amb LoRa (9 de gener de 2021)
Curset introductori d'Internet de les Coses per ADTelecom (Comença el 5 de novembre de 2020)
Ús de les dades generades pels sensors LoRaWAN i arquitectura del sistema. Rubí, 17 de juny de 2020
Curset a TE Connectivity del 4 de març de 2020 a TE Connectivity
Introducció ràpida a LoRaWAN i The Things Network (Ajuntament de Viladecans, 19 de febrer de 2020)
UPC-School - Màster Industria 4.0 Tecnologías IoT, Hands on y MVP (2020)
UPC-School - 21802500 - Màster Industria 4.0 Tecnologías IoT, Hands on y MVP (2019)
Introducció ràpida a LoRaWAN i The Things Network a l'Institut de Ciències del Mar (27 / setembre / 2018 i 25 / setembre / 2019)
Introducció a Internet de les Coses - juny 2018 (Curset de formació per a professors de CF realitzat a l'Institut Rambla Prim)
Xifratge
Opinió
Hacia un Internet de las Cosas democrático y efectivo per Xavier Pi (octubre 2018)